There are many parasitic forms that enter and live in the human body. Infection with worms in children is one of the most common illnesses. Usually their severity is underestimated. They remove nutrients from babies' food, cause allergies, intractable poisoning, reduce immunity and damage abdominal organs.

According to statistics, more than half of the population is infected with parasites, and among children there are many more infected. The early stage of the disease passes without symptoms - in a latent form. Worms in children, the symptoms and treatment of which parents need to learn and understand, sometimes live in a person for many years, do not manifest themselves in any way and activate only with a decrease in immunity.
Spread of worms
The diseases that cause the lower worms are called helminthiasis. No one is safe from them, often the infected themselves are to blame for the appearance of the worms. The climate has the greatest influence on the degree of their prevalence. They are more comfortable in hot tropical countries. The number of parasites also depends on the socio-economic level: in underdeveloped regions with a low level of hygiene and medicine, many people mainly suffer from helminth infestations.
It is generally accepted that helminthiasis is a disease characteristic of lower social strata living in unsanitary conditions, having frequent contact with the earth or animals - carriers of invasions. However, statistics refute this claim: in prosperous European countries, the examination finds worms in a third of patients.
2 million cases of infection are diagnosed each year, and the figure of 20 million is based on sales of anthelmintic drugs. 80% of them are children. Helminths are viable, fertile, a female lays 200, 000 eggs per day.
Types of worms
There are a large number of types of worms - more than 300, of which 70 are typical of our region, the rest are brought by travelers from exotic countries. All types of parasites suitable for inhabiting the human body belong to three main categories:
- nematodes belonging to the class of round worms, most often seen in babies (these include pinworms, whipworms, Trichinella, roundworms);
- adhesive (flat) worms, classified as cestodes (these include tapeworms, tapeworms, echinococci);
- trematodes or fluke parasites that live and reproduce in the intestine, but can be delivered through the bloodstream to various human organs. Usually, the intestines, liver, and gallbladder adjacent to the stomach are most infected, but the worms reach muscle tissue, lungs, and even the brain and heart.
First, in terms of prevalence, there are pinworms, which have a round diameter and tiny parameters - no more than 6 mm. They are located in the lower part of the colon. More than 24, 000 species of nematodes are known. The female can lay 150, 000 eggs per day. Their systematic movement and reproduction outside the intestine is the main reason for the risk of secondary infection with enterobiasis.
Roundworm infestation, which ranks second in terms of distribution, is inherent in preschool children and young schoolchildren. The adult worms look threatening: they grow up to 30 cm, and the female lays about 100, 000 eggs per day. The larvae enter the body through unwashed hands, dirty food and water. They are transmitted by the bloodstream to all parts of the child's body and settle there. This type of helminthiasis is quite dangerous for the body of an untrained child. Ascariasis is often the culprit of an allergic reaction in children.
Trichinella is not that common in children. These are the causative agents of trichinosis, characterized by the lightning-fast transfer of eggs through the body, causing damage to muscle tissue. The consequences of trichinosis are peritonitis, intestinal bleeding.
Sources and methods of invasion
Prevention of helminth infection in children is possible if you understand the information about the transmission of worms. In fact, there are several possibilities for their penetration into the human body. Most of it reaches a person through household or food contact.
Many believe that strict observance of the principles of personal hygiene will protect against helminthiasis. Unfortunately, this opinion is wrong. Children are most at risk of infection due to close contact with the culprits. Each of the sources of invasion has its own characteristics:
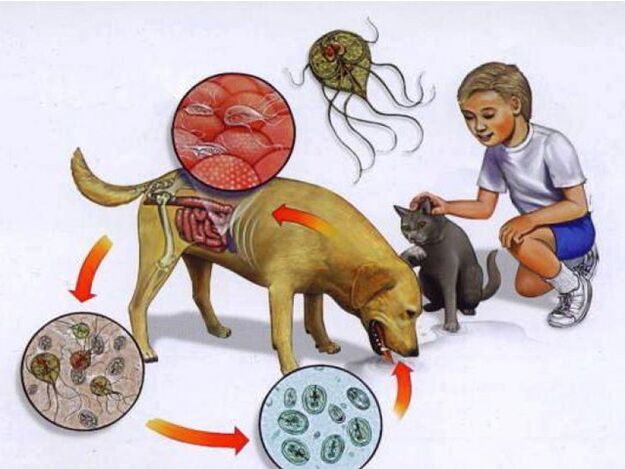
- with the contact-household route, the larvae enter the body through infected people, objects, animals;
- with the food method, the culprits are unwashed palm trees, water of questionable purity, infected food;
- with the path of transmission, the worms come from blood-sucking insects;
- with active (percutaneous) - the testes of the worms overcome the connective tissues or skin of the soil or reservoirs during the bathing process. Sometimes larvae in the air, as well as dust particles, enter the respiratory system.
Despite the diversity of worm species, children are infected with them in much the same way. Eggs, larvae, part of the body or a whole parasite, when it reaches a person, begin to feed and reproduce, their number in the absence of treatment increases sharply. The state of health of an infected person worsens, he becomes the culprit for the transmission of the invasion to others.
The eggs of the most common helminths - roundworms, pinworms, covered with a sticky capsule, firmly adhere to the surface and are held there. The spread occurs quite early. Once on the palms and fingers, the eggs collect under the fingernails, from where they are transferred to everyday objects that a person uses. This is how all family members and the immediate environment are infected.
Certain types of worms are able to enter the placenta and infect the fetus in utero. Obtain an infestation from a mother suffering from enterobiasis, possibly during childbirth. A breastfeeding child can be infected by sick parents, although the disease is not transmitted through breast milk. There are also non-standard cases of transmission of eggs from worms from an infected person: during sexual contact or kissing, and contraception in this case is unnecessary.
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from helminthiases: their larvae live everywhere. However, there is a possibility of reducing the risk of disease for those who comply with hygienic requirements, eat food that has undergone heat treatment, and regularly undergo preventive treatment against worms.
Identification of helminths
Infection with parasites most often occurs in the hot season, as babies vigorously explore their surroundings, spend all day outdoors in the sandbox, splash around in tanks, feast on berries and fruits directly on them. branches, without worrying about washing your hands and fruit.
In adults, worms, before entering the body, need to force a number of obstacles: saliva in the mouth, acidic environment in the stomach, intestinal immune defenses. In children, the protection is much weaker, which is why helminths overcome it more easily. Parents should be aware of the signs of infestation in their children. Most of them are aware of a difference such as teeth grinding at night, although this is not the only indicator. How to understand that a child has worms? You have to watch out for the symptoms.
Common symptoms of worms
The presence of helminths in the child's body poisons it with wastes, which is why one of the main symptoms of infection is considered to be increased fatigue, dizziness, refusal to eat, whims. The following general characteristics are characteristic:
- allergic skin reaction - rashes, hives, eczema;
- digestive complications - alternating constipation and diarrhea, bloating, nausea, navel pain;
- decrease in protective immunity, repeated colds, addition of fungal infection;
- manifestation of an allergic-toxic response to vaccination;
- low hemoglobin levels.
Parents should be especially vigilant about the complexity of these signs in a baby, for example, when acute respiratory infections or thrush are difficult to cure. In such cases, it is logical to assume the presence of an invasion of helminths.
In addition to the general symptoms of infection with worms, there are individual signs of the presence of a certain parasite in a child.
Symptoms of Ascaris
The key symptom of ascariasis in children is a dry cough with worms in children, associated with a rash, and two weeks later - the manifestation of general indicators of intoxication, pain in the abdominal cavity. A distinctive signal is the variability of the nervous and mental well-being of the child.
Symptoms of pinworms
Pinworm infection is declared as dehydration of the oral cavity. Infected children complain of irritation in the anal area, especially at night. The child scratches this surface, which is heavy with inflammation. In girls, these symptoms are supplemented by enuresis and vulvovaginitis. The appetite changes, the stools are upset, the baby is coughing, does not sleep well, his nervous system is upset.
Manifestation of signs of other worms
Trichocephalosis is common in temperate and subtropical climates: whipworms prefer humidity. The signs are not quite typical: the pain resembles attacks of appendicitis, the baby often has an urge to defecate, and symptoms of colitis are seen. The consequence can be rectal prolapse, as well as severe anemia.
Hookworms love humidity, heat, they also prefer subtropical and tropical climatic regions, in particular - the Krasnodar Territory. One symptom is a rash where the parasite enters the skin. Complicated by severe anemia.
Dogs are carriers of toxocariasis, the disease spreads everywhere. The symptoms are:
- pain in the abdominal area;
- decreased vision;
- nervous system disorder;
- allergic reactions.
It can be complicated by bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchial asthma.
Echinococcosis breeds everywhere - on every continent except Antarctica. For a long time it is latent, the symptoms are nervous disorders, headaches. The serious consequences are disturbances of the brain, lungs, liver, heart and kidneys. Helminthic invasion in children, the symptoms of which are life threatening, is treated with surgery.
Trematosis (opisthorchiasis, fascioliasis) is widespread on the coasts of seas, in river basins, the main source of infection is non-heat-treated fish. Symptoms of the disease are characterized by jaundice, muscle pain, fever, and allergic rash. The disease is aggravated by ulcerative gastroduodenitis, cirrhosis of the liver, purulent cholangitis, peritonitis, chronic hepatitis.
The symptoms of childhood helminthiasis are polymorphic, the signs are suitable for many diseases, so it is difficult to use only the clinical picture for diagnosis. More real results are obtained by laboratory research - an analysis of worm eggs, and it must be repeated several times.
Age characteristics of the disease
Worms in an infant
Usually, helminths are found in preschool children of one and a half or two years. Babies are rarely infected with parasites from an infected mother - during intrauterine development, at the time of childbirth, during feeding. This usually occurs after 6 months, with the onset of complementary feeding, an active crawling motion. The child does not miss a single microbe, bacterium, parasite. It is much more difficult to detect helminths in infants than in children of a different age. Symptoms and signs of worms in children are:
- child anxiety, disturbed sleep;
- constant fatigue, lethargy, general weakness;
- irritation and inflammation in the anal area, and in girls - around the genitals;
- digestive disorders: constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, gas, colic;
- dizziness associated with intoxication of the body;
- weight loss, refusal to eat, although there are exceptions;
- pallor, white tint of the skin,
- shadows under the eyes;
- rashes on the body, mainly on the thighs;
- insignificant increase in temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- regular cough, independent of respiratory disease.
Such symptoms in an infant can signal not only an invasion of helminths, but also many other diseases. That is why, in order to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a fecal examination several times at a certain interval.
Symptoms of worms in 2 year olds are mostly similar to common signs of worms. The introduction of larvae and developing forms of worms into the child's body can cause serious damage to health, because in babies the defenses are just beginning to form, the child is not ableto resist unwanted aggressors. The risk is increased by the fact that children are ready to taste everything without any knowledge of the principles of hygiene. Regardless of the type of worms, the manifestations of helminthiasis in children from two years old are similar. This:
- rash on the skin;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- profuse discharge of saliva at night during sleep;
- a sudden increase or decrease in appetite, accompanied by a decrease in body weight;
- unexpected nausea, intestinal dysfunction.
There are also common signs: irritation of the anus, in girls - in the genital area, intoxication, fatigue, decreased immunity, disturbance of nervous processes.
Symptoms of worms in children from 3 years old are identical to the previous ones.
An important factor in the invasion of children aged 3 to 5 is their visit to day care centers, as well as contact with animals infected with worms. Children are infected with rarer pathogens of helminthiasis when they travel to exotic countries or from relatives who have stayed there. The rapid penetration of larvae, parasite eggs into the child's body is facilitated by:
- deficiency of vitamins, useful elements;
- lack of dietary protein;
- poor quality food;
- reduced immunity.
Symptoms of worms in 5-year-old children are similar. On Dr. Komarovsky's website, you can see photos and videos about the treatment and prevention of worms, as well as read patient reviews.
Diagnosis of the disease
The appearance of the first symptoms suggesting a helminthic invasion signals the need for special studies. In clinical practice, sufficient attention is paid to the diagnosis of helminthiasis in preschool children and elementary school students. The presumptive diagnosis must be confirmed by laboratory research techniques:
- a clinical blood test, which defines the task of finding antibodies against certain pathogens of parasites;
- scraping for enterobiasis and analysis of feces, carried out three times in order to correctly diagnose;
- an analysis that evaluates the intestinal microflora.
On a general blood test, they look at the color indicator. The diagnosis is confirmed provided that its index is higher than the established one, the number of eosinophils is increased, hemoglobin, on the contrary, is reduced and anemia is expressed. A blood test for an enzyme immunoassay for parasites is done on an empty stomach in a vein. The effect is almost one hundred percent unmistakable, reliable, it is even able to identify the type of worms, the damage to the baby's body from worms.
Analysis of helminth eggs and dysbacteriosis is carried out on the basis of a study of feces. Stool tests for worms do not always give a result, which is why they are done repeatedly. To detail the diagnosis, a biological study of sputum, bile, urinalysis and feces is used. Opisthorchiasis is determined by examining the contents of the intestine and duodenal intubation.
Additional diagnostic techniques include ultrasound of internal organs, x-rays, computed tomography, MRI. They help the specialist to determine the presence of helminths in internal organs. The combination of these studies makes it possible to confirm or refute the diagnosis of enterobiasis. The sooner the diagnosis is made and treatment for worms in children is started, the less the health of the baby will be affected.
Healing of invasions by the traditional method
The serious consequences of helminthiasis make us take a responsible approach to the treatment of the disease, contacting specialists - a parasitologist or a pediatrician. The medical treatment consists of 3 stages.
The preparatory stage is the appointment of absorbents and antihistamines to cleanse the baby's body from toxic substances that have accumulated as a result of the life cycle of parasites.
Anthelmintic therapy consists of the selection of drugs depending on the age, type of pathogens and stage of the disease. Usually, a single reception of the drug in the form of a tablet or suspension is prescribed. After 2 weeks, the course is repeated.
Anthelmintic drugs are very toxic, therefore, when prescribing them, care should be taken as much as possible so as not to harm the health of the child. Moderation of dosage is of paramount importance. Self-medication is not recommended, the drug must be prescribed by a doctor, who may sometimes prescribe a combination of drugs. It is recommended to carefully read the contraindications of the anthelmintic agent.
The cleaning scheme is carried out after the use of anthelmintic drugs, when the parasites die off, leaving the body with feces. At this moment, there is a huge splash of toxic substances in the baby's body. For cleaning, enemas are prescribed, the intake of absorbents and choleretic drugs. After the end of treatment, it is necessary to repeat blood and stool tests. If there are any complications, the baby is registered for 3 years.
Folk remedies
Herbal healers have a long history of salvation from parasitic worms. Traditional medicine recognizes the benefits of some of these remedies. However, not all of them give a guaranteed result. It is advisable to coordinate their use with a doctor. The following folk recipes are considered the most effective:

- use pumpkin seeds;
- the use of hemp, pumpkin, linseed oil;
- garlic enema with the addition of milk;
- use a soda enema;
- carrot juice;
- tansy infusion: 3 tbsp. L. tansy is poured with a glass of boiling water, insisted for an hour, the infusion is given to the child to drink 1 liter of dessert. three times per day; overdose is unacceptable so that there is no depression of the nervous system;
- birch tar;
- herbal infusions, wormwood enemas.
Preventive measures
To protect a child from helminthic invasions, certain rules must be strictly observed:
- teach the baby to wash his hands well before eating, after a walk;
- systematically cut the nail plates;
- change the child's costume more often;
- keep clean household items, toys;
- it is undesirable to keep tetrapods in the house;
- learn not to take your fingers, toys in your mouth for a walk;
- once a year to carry out prophylaxis for the whole family in the form of medication.
The worm infestation is a serious problem. The disease is quite common in the world, children are particularly susceptible to it. The disease can last for years and cause enormous damage to the health of the baby. Worms release toxins during their existence, leading to the onset of various diseases that give the child a lot of discomfort and unpleasant sensations. That is why parents should notice the symptoms in time, undergo treatment with the help of a specialist.






































